Nội Dung Chính
Page 124
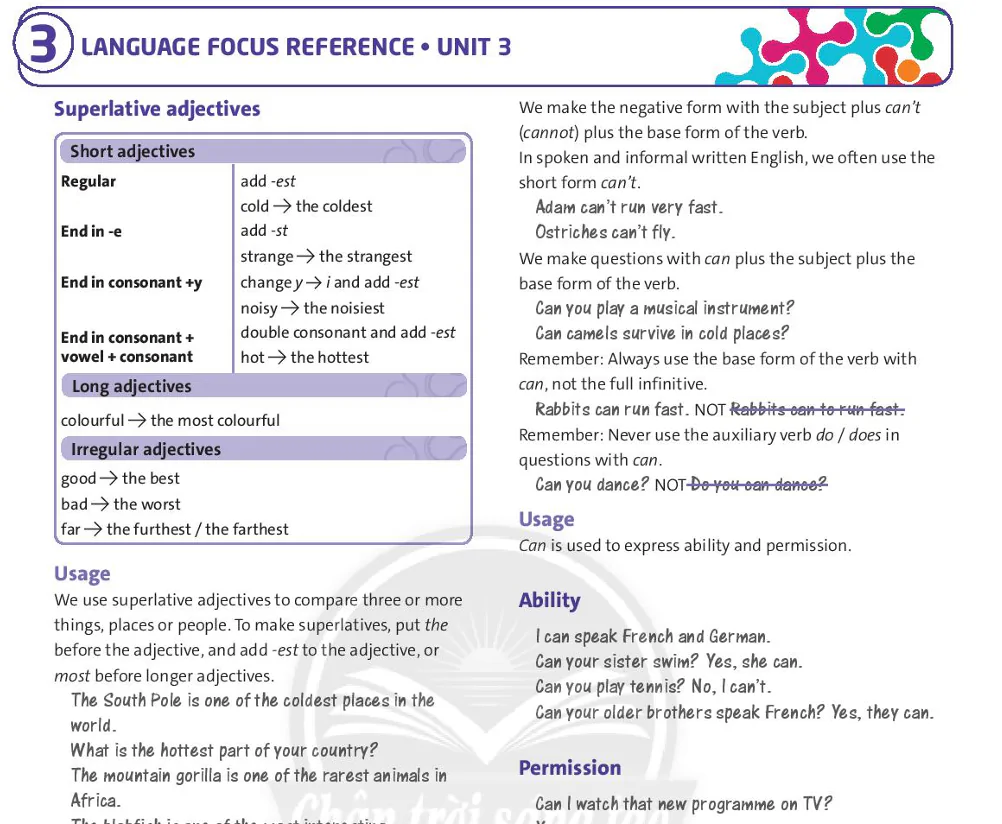
Present simple: affirmative and negative
| Affirmative | Negative |
| I help at home. He helps at home. We help at home. | I don't help at home. He doesn't help at home. We don't help at home. |
The affirmative form is the base form of the verb (infinitive without to). To make the third person singular (he / she / it), add -s or -es, or for verbs ending in -y, remove -y and add -ies.
| I sing | she sings |
| you go | he goes |
| we study | he studies |
To make the negative form, use do not or does not plus the base form of the verb.
In spoken or informal written English, we use the short forms don't or doesn't.
I don't get home late.
He doesn't get home late.
Present simple: questions
| Questions | Short answers | |
| Affirmative | Negative | |
| Do I wash the car? Do you wash the car? Does he wash the car? Does she wash the car? Does it wash the car? | Yes, I do. Yes, you do. Yes, he does. Yes, she does. Yes, it does. | No, I don't. No, you don't. No, he doesn't. No, she doesn't. No, it doesn't. |
Do they play video games? Yes, they do.
Do you watch TV a lot? No, I don't.
To make the question form, use do or does plus the subject plus the base form of the verb.
We make short answers with do or does in the affirmative and don't or doesn't in the negative.
| Question word | Auxiliary verb | Subject | Verb |
| What Where When Who What time How often | does do does do does do | she you Harry they the film you | play? study? get up? like? start? watch TV? |
Put question words at the beginning of the question.
Where does he work?
Remember to include the auxiliary verb do / does in questions.
Where do you live? NOT Where you live?
Usage
We use the present simple:
1. to talk and ask questions about habits, routines and things that happen regularly.
What time do you get up?
Fatma eats breakfast at 8 a.m.
2. to describe things that are always true, or almost always true.
I live in Kiev. My teacher doesn't speak French.
3. to talk about what we think, feel or like.
Do you like Turkish music? We love Italian food.
Adverbs of frequency
always 
normally, usually

often 
sometimes 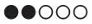
rarely 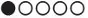
never 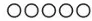
In sentences with be, adverbs of frequency go after the verb be.
Robert is always friendly.
However, with all other verbs, adverbs of frequency go before the verb.
They often help with the housework.
In questions, adverbs of frequency always go after the subject.
Do you usually wash your face in the morning?
Are your brothers always noisy?
Usage
We use adverbs of frequency to describe how often we do something.
































Bình Luận
Để Lại Bình Luận Của Bạn