Nội Dung Chính
Page 120
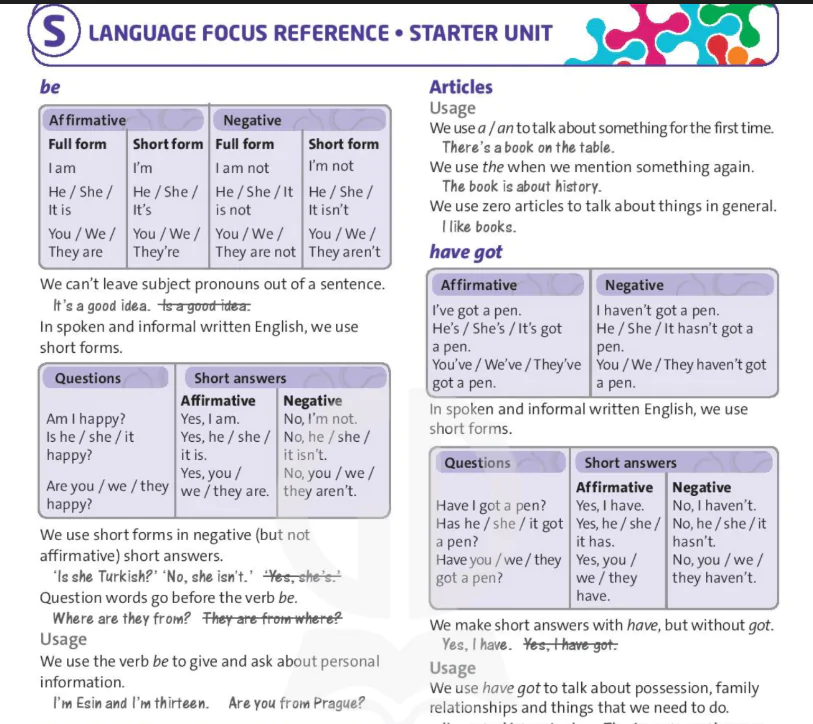
Present continuous: affirmative and negative
| Affirmative | Negative |
| I'm talking. He / She / It's talking. You / We / They're talking. | I'm not talking. He / She / It isn't talking. You / We / They aren't talking. |
We make the affirmative form of the present continuous with the verb be and the -ing form of the main verb.
We make the negative form with the verb be plus not and the -ing form of the main verb.
In spoken and informal written English, we use short forms.
I am writing. → I'm writing.
He isn't talking.
Present continuous: questions
| Questions | Short answers | |
| Negative Yes, I am. Yes, he / she / it is. Yes, you / we / they are. | Affirmative No, I'm not. No, he / she / it isn't No, you / we / they aren't. | |
We make the question form by inverting the verb be and the -ing form of the main verb.
We make short answers with the verb be without the -ing form of the main verb.
We don't use short forms in affirmative short answers.
'Are you studying?' 'Yes, I am.' 'Yes, I'm.'
'Is Selin watching TV?' 'Yes, she is.' 'Yes, she's.'
'Are we doing this exercise?' 'Yes, we are.' 'Yes, we're.'
Question words go before the verb be.
What are you talking about?
Who are you messaging?
Why are they laughing?
Where's Lenka going?
Present simple and present continuous
Usage
We use the present continuous to talk about an action in progress. We use it for things which are happening now or around now. We often use time expressions like now, right now or at the moment with the present continuous.
'Is Alicia doing her homework now?' 'Yes, she is.'
'Where's Osman right now?' 'He's chatting online.'
'They're studying for their history exam at the moment.
We use the present simple to talk about routine or repeated actions. We often use adverbs of frequency like always, usually, often, sometimes or never with the present simple.
Do you often post messages on social media?
She always watches that TV programme.
Ollie sometimes uses instant messaging.
I never send emails.
There are some verbs (stative verbs) which we don't normally use in the continuous form because they describe states which are true, not actions in progress. These include: understand, know, believe, think, mean, like, dislike, love, hate, want and prefer.
We don't understand this question.
We aren't understanding this question.
What does that word mean?
What is that word meaning?
I like your new mobile phone.
I'm liking your new mobile phone.
Do you want a coffee?
Are you wanting a coffee?

































Bình Luận
Để Lại Bình Luận Của Bạn