Nội Dung Chính
Page 122
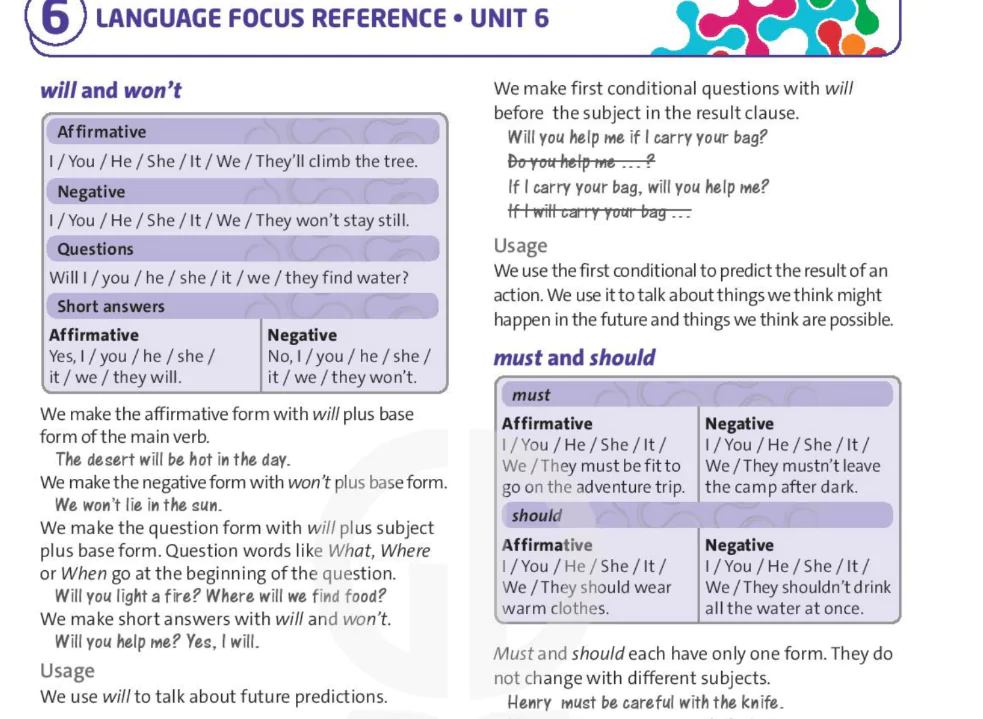
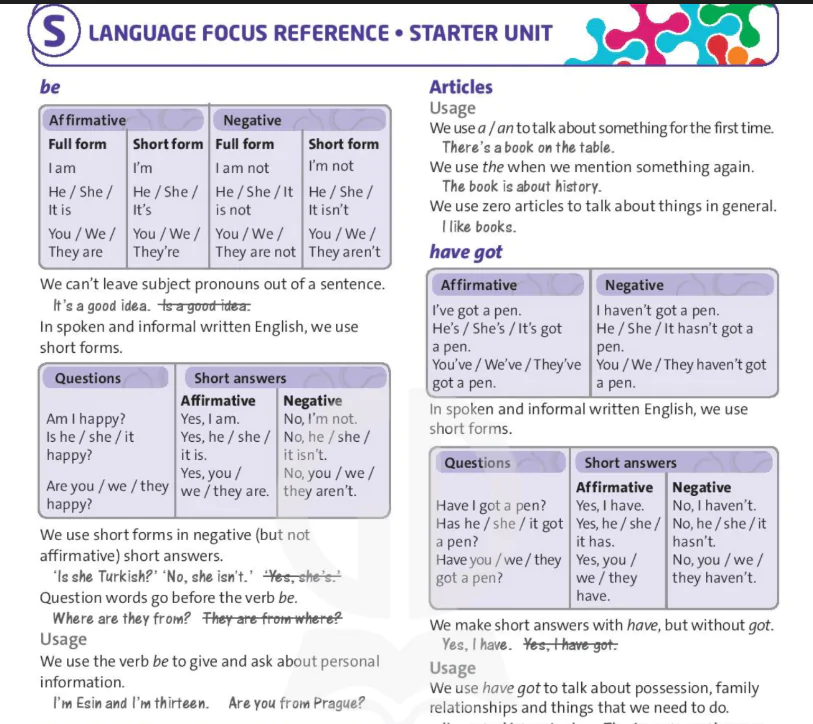
Past continuous: affirmative and negative
| Affirmative | Negative |
| I was jumping. He / She / It was jumping. You / We / They were jumping. | I wasn't jumping. He / She / It wasn't jumping. You / We / They weren't jumping. |
We make the affirmative form of the past continuous with was or were and the -ing form of the main verb.
We make the negative form by putting not between was or were and the -ing form of the main verb.
In spoken and informal written English, we use the short forms wasn't and weren't.
Past continuous: questions
| Questions | Short answers | |
| Affirmative | Negative | |
| Was I climbing? Was he / she / it climbing? Were you / we / they climbing? | Yes, I was. Yes, he / she/ it was. Yes, you /we / they were. | No, I wasn't. No, he /she / it wasn't. No, you / we / they weren't. |
We make short answers with the subject and was or were, without the -ing form of the main verb.
Were you walking to school at 8.00? Yes, I was.
Was Selin standing in that photo? No, she wasn't.
Were they running on Friday? Yes, they were.
Question words go before the verb was or were.
What were we doing on Saturday morning?
Where was Artem walking this afternoon?
Usage
We use the past continuous to talk about actions in progress at a point in the past. We often use expressions to show the point of time, such as at or on (plus a time) or when (plus a past simple action).
It was raining at two o'clock this morning.
What were they doing on Friday evening?
You weren't listening to the photographer when he said 'smile'.
Past simple and past continuous
Usage
We often use the past continuous to describe an action in progress which was interrupted.
She was walking into town when she met her friends.
We use the past continuous for the longer action in progress (was walking). We use the past simple (met) for the shorter action which interrupts the longer one.
We often use when before the past simple and while before the past continuous.
They were travelling across Africa when they took the photo.
They took the photo while they were travelling across Africa.
Adjectives and adverbs
| Most adjectives | add -ly polite → politely, slow → slowly, quiet → quietly |
| Adjectives ending in -y | drop -y and add -ily happy → happily, easy → easily, angry → angrily |
| The same as the adjective | hard → hard, fast → fast |
| Irregular | good → well |
Usage
We use adjectives to describe nouns.
Mike is a polite boy.
We use adverbs to describe verbs.
Mike speaks politely.
































Bình Luận
Để Lại Bình Luận Của Bạn