Page 124
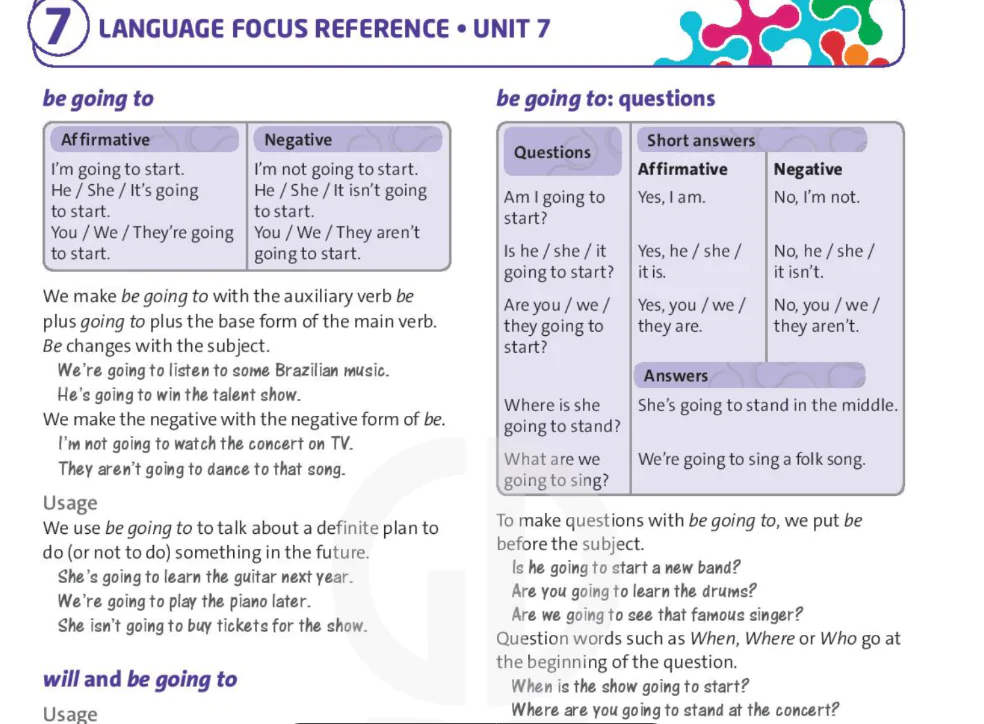
will and won't
| Affirmative |
| I / You /He / She /It / We / They'll climb the tree. |
| Negative |
| I / You / He / She / It / We /They won't stay still. |
| Questions |
| Will I/you/he/she/it / we / they find water? |
| Short answers |
| Affirmative | Negative |
| Yes, I / you / he / she/ it / we / they will. | No, I / you / he / she / it/ we / they won't. |
We make the affirmative form with will plus base form of the main verb.
The desert will be hot in the day.
We make the negative form with won't plus base form.
We won't lie in the sun.
We make the question form with will plus subject plus base form. Question words like What, Where or When go at the beginning of the question.
Will you light a fire? Where will we find food?
We make short answers with will and won't.
Will you help me? Yes, I will.
Usage
We use will to talk about future predictions.
will and won't in the first conditional
| Action | Result |
| If I climb a tree, If he / she / it eats the fruit, If you / we / they follow the river, | I'll be safe. he/she / it'll feel ill. you / we / they'll find the village. |
| Result | Action |
| I'll be safe. | if I climb a tree. |
We make the first conditional with two clauses: the action clause (If clause) with the present simple and the result clause (main clause) with will.
Conditional sentences can start with the action:
If you light a fire, you'll feel warmer.
or with the result:
You'll feel warmer if you light a fire.
We can use the negative form in the action, the result, or both parts of the sentence.
We won't win the challenge if we get lost in the trees.
If he doesn't have a compass, he'll get lost.
If we don't make a big noise, we won't find help.
We make first conditional questions with will before the subject in the result clause.
Will you help me if I carry your bag?
Do you help me...?
If I carry your bag, will you help me?
If I will carry your bag...
Usage
We use the first conditional to predict the result of an action. We use it to talk about things we think might happen in the future and things we think are possible.
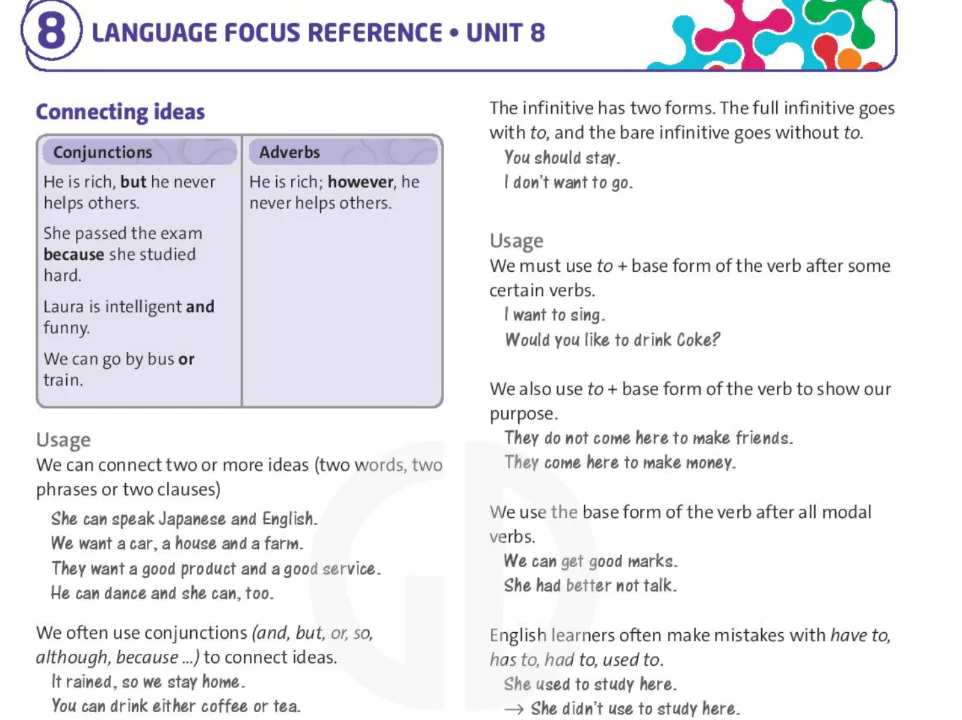
must and should
| must |
| Affirmative | Negative |
| I / You / He / She / It / We / They must be fit to go on the adventure trip. | I / You / He / She / It / We / They mustn't leave the camp after dark. |
| should |
| Affirmative | Negative |
| I / You / He / She / It / We / They should wear warm clothes. | I / You / He / She / It / We / They shouldn't drink all the water at once. |
Must and should each have only one form. They do not change with different subjects.
Henry must be careful with the knife.
Henry musts be careful with the knife.
She should take a sleeping bag.
She shoulds take a sleeping bag.
We use must / should plus base form of the main verb.
You must listen now. They should sit here.
You must to listen now. They should to sit here.
The negative forms of must and should are must not and should not. In spoken and informal written English, we use the short forms mustn't and shouldn't.
As with must and should, the main verb takes the base form.
We mustn't touch this. We mustn't to touch this.
You shouldn't drink that. You shouldn't to drink that.
Usage
Should is for giving advice and recommendations.
You should take a first-aid kit with you. It's a good idea.
You shouldn't buy that torch. It's expensive.
Must is for talking about strong obligations.
You must wear shoes in the jungle. It's really important.
You mustn't eat those leaves. They're very bad for you.































Bình Luận
Để Lại Bình Luận Của Bạn